Commits on Source (3)
-
Javier Valdes authored
-
Javier Valdes authored
Showing
- README.md 40 additions, 72 deletionsREADME.md
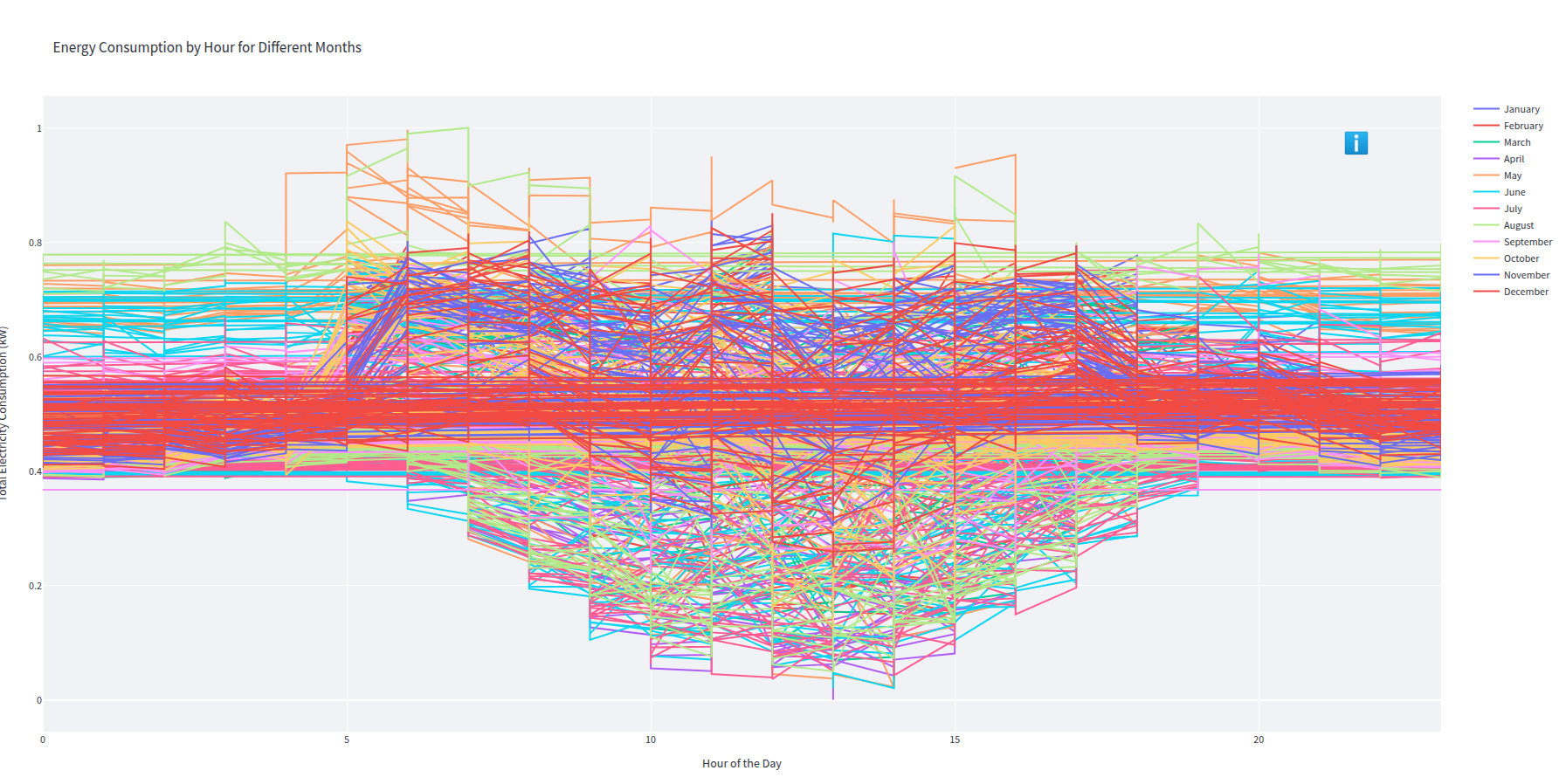
- Screenshot from 2025-03-03 14-19-33.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsScreenshot from 2025-03-03 14-19-33.png
- better-implem.py 1 addition, 1 deletionbetter-implem.py
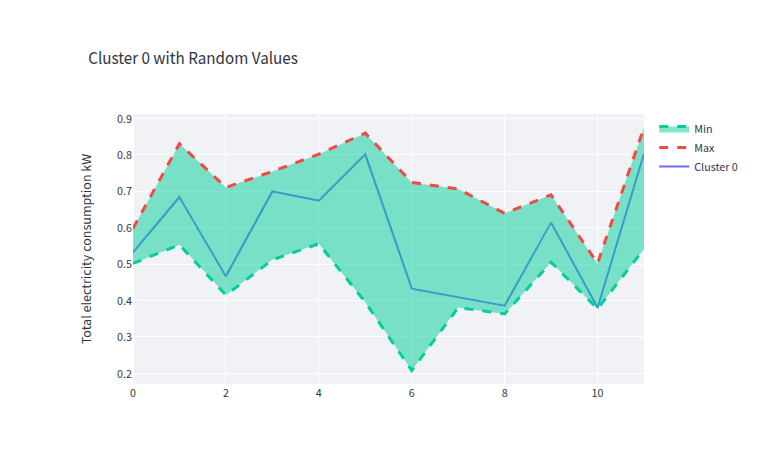
- clust_0_data_gen.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclust_0_data_gen.png
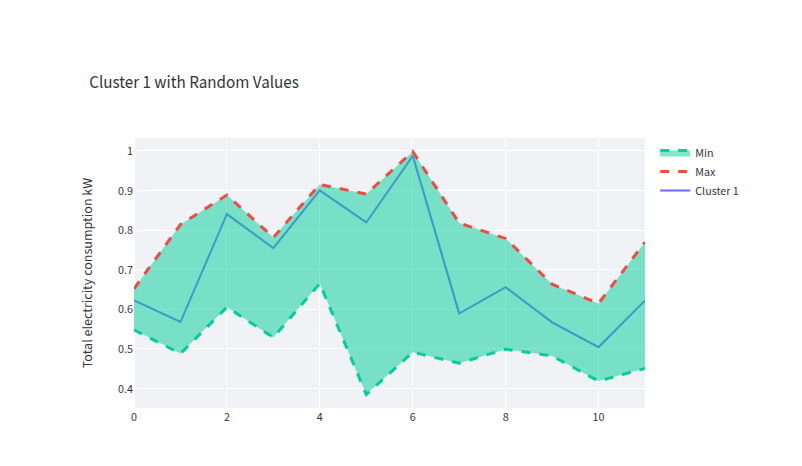
- clust_1_gen_data.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclust_1_gen_data.png
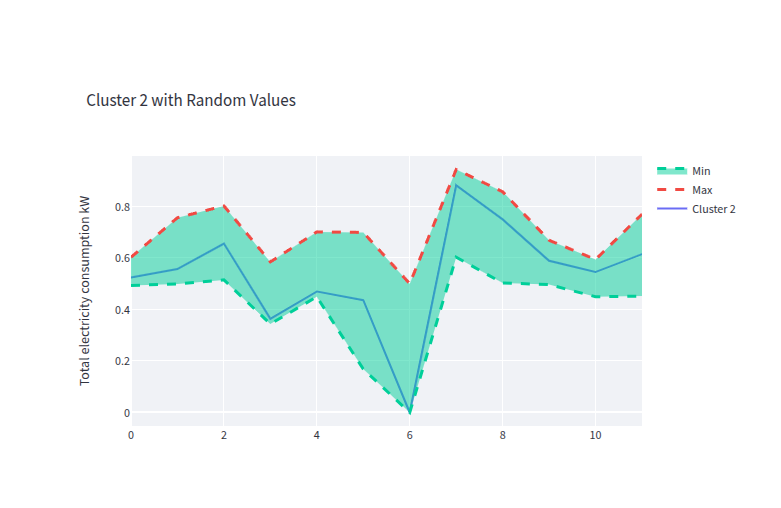
- clust_2_gen_data.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclust_2_gen_data.png
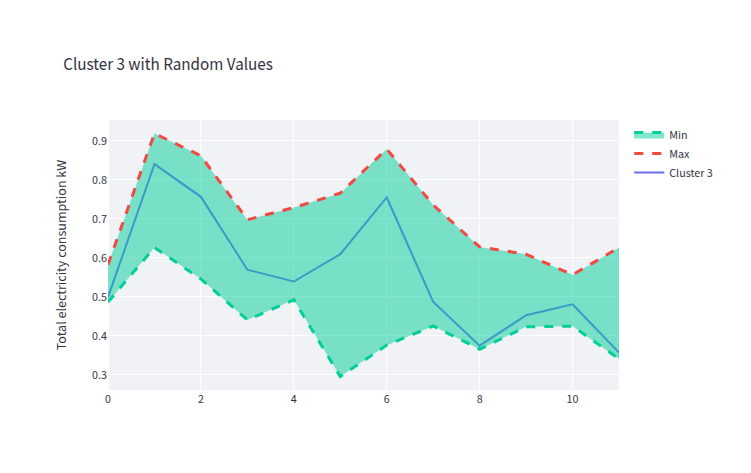
- clust_3_gen_data.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclust_3_gen_data.png
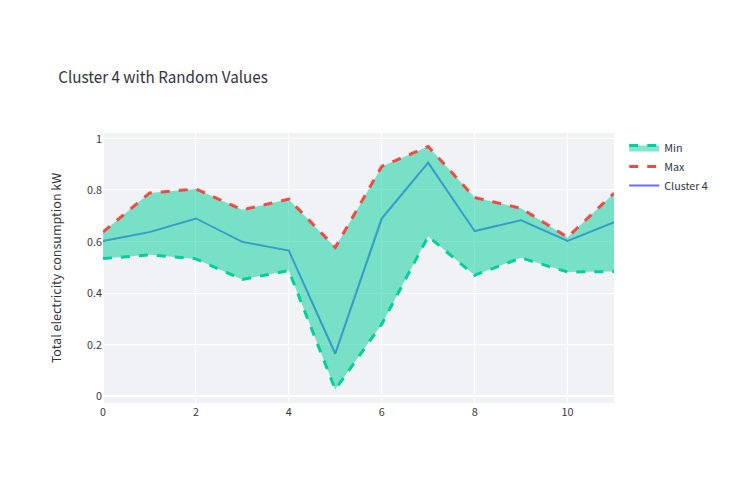
- clust_4_gen_data.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclust_4_gen_data.png
- clustering_cvi.csv 1 addition, 1 deletionclustering_cvi.csv
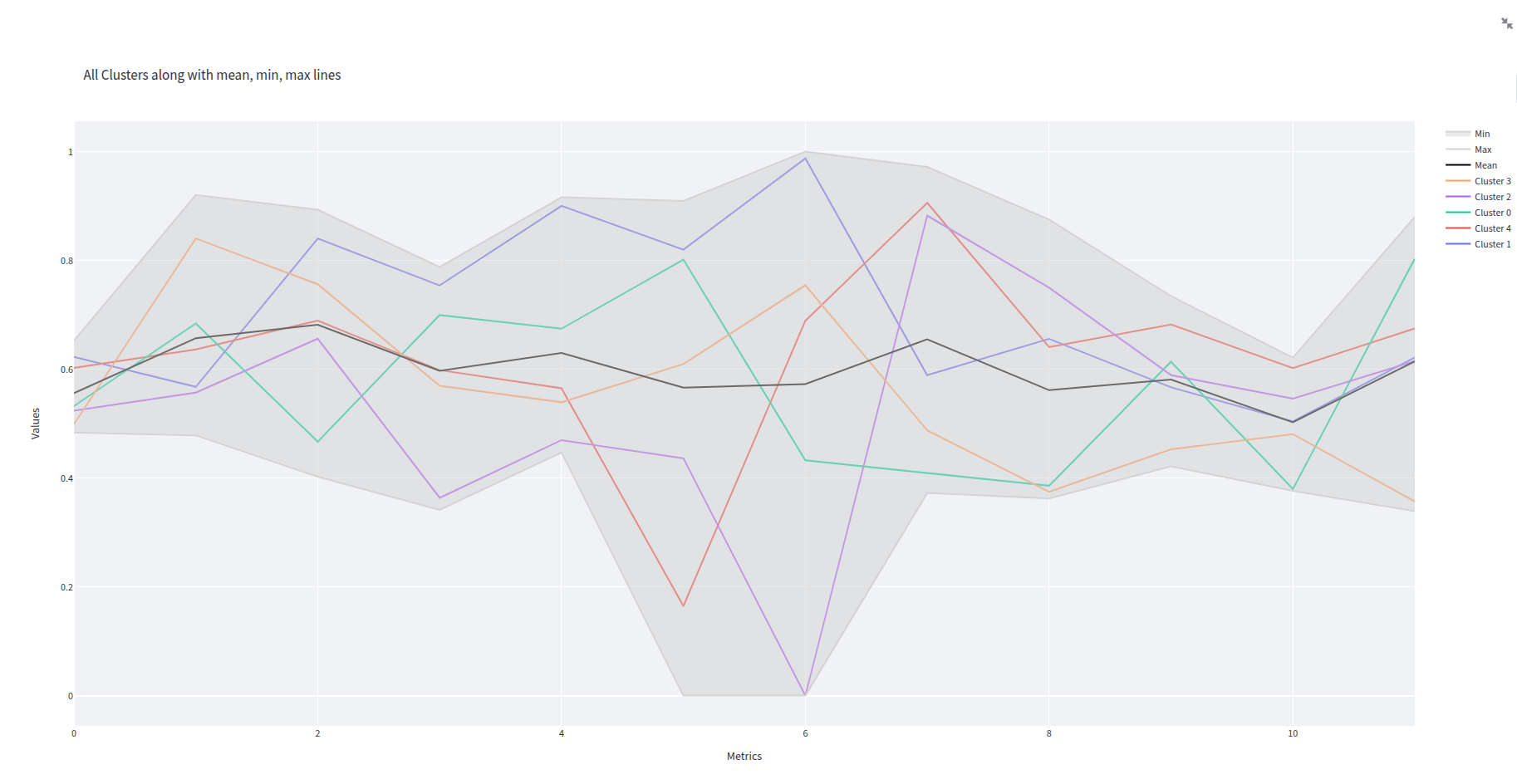
- clusters_plot.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsclusters_plot.png
- dashboard.py 1165 additions, 0 deletionsdashboard.py
- data/1.1_Working_With_Clustering_Tool_Default_Parameters · Wiki · TCF-SPATIALAI _ Clustering-tool · GitLab.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletions...ers · Wiki · TCF-SPATIALAI _ Clustering-tool · GitLab.pdf
- data/1.2_Working_With_Clustering_Tool_User_Parameters · Wiki · TCF-SPATIALAI _ Clustering-tool · GitLab.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletions...ers · Wiki · TCF-SPATIALAI _ Clustering-tool · GitLab.pdf
- data/B_sc_Thesis.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsdata/B_sc_Thesis.pdf
- data/B_sc_ThesisSecondDraft.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsdata/B_sc_ThesisSecondDraft.pdf
- data/fenecon_de/Anlagenbauer.csv 35042 additions, 0 deletionsdata/fenecon_de/Anlagenbauer.csv
- data/fenecon_de/Apotheken.csv 35042 additions, 0 deletionsdata/fenecon_de/Apotheken.csv
- data/fenecon_de/Autohaus 2.csv 35042 additions, 0 deletionsdata/fenecon_de/Autohaus 2.csv
- data/fenecon_de/Autohaus.csv 35042 additions, 0 deletionsdata/fenecon_de/Autohaus.csv
- data/fenecon_de/Bauhof 2.csv 35042 additions, 0 deletionsdata/fenecon_de/Bauhof 2.csv
Screenshot from 2025-03-03 14-19-33.png
0 → 100644
912 KiB
clust_0_data_gen.png
0 → 100644
44.2 KiB
clust_1_gen_data.png
0 → 100644
41.1 KiB
clust_2_gen_data.png
0 → 100644
40.1 KiB
clust_3_gen_data.png
0 → 100644
43.1 KiB
clust_4_gen_data.png
0 → 100644
37.7 KiB
clusters_plot.png
0 → 100644
175 KiB
dashboard.py
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
File added
File added
data/B_sc_Thesis.pdf
0 → 100644
File added
data/B_sc_ThesisSecondDraft.pdf
0 → 100644
File added
data/fenecon_de/Anlagenbauer.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/fenecon_de/Apotheken.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/fenecon_de/Autohaus 2.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/fenecon_de/Autohaus.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/fenecon_de/Bauhof 2.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.